The US dollar staged a "Jedi counterattack", what did Powell say?
2025-09-18 13:44:57

The Federal Reserve announced its interest rate decision, monetary policy statement and revised Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) at 2:00 a.m. Beijing time on Thursday (September 18), followed by a press conference by Federal Reserve Chairman Powell at 2:30 a.m. Beijing time on Thursday.
Key Points from Powell's Press Conference
Inflation has recently risen and remains elevated. The slowdown in GDP growth primarily reflects a decline in consumer spending. Wage employment growth has slowed significantly, reflecting lower immigration and declining labor force participation. Labor demand has weakened. Employment growth is below the break-even level.
Inflation has retreated from its peak in mid-2022 but remains elevated. The headline PCE price index likely rose 2.7% year-on-year in August, with the core PCE index rising 2.9%. Goods inflation has risen, while services inflation continues to moderate. Beyond next year, most indicators of inflation expectations are consistent with our 2% target.
Policy changes are gradually emerging, and their economic impact remains unclear. The overall impact of tariffs on inflation remains to be seen. The ongoing inflationary risks posed by tariffs need to be managed and assessed. The balance of risks has shifted. We are well-positioned to respond promptly. Potential tariffs are one factor contributing to the slowdown in the job market. Price increases this year are the primary cause of rising inflation. Tariff-induced price increases are expected to continue this year and next.
Changes in the labor market are primarily due to changes in immigration policy. Labor demand has declined slightly more than labor supply. Policies have remained restrictive this year. The labor market can no longer be described as robust. Risks are becoming more balanced. The shift in the balance of risks suggests a need for a neutral adjustment. There is widespread opposition to a 50 basis point interest rate cut. There is no need to rush into adjusting interest rates. This rate cut can be viewed as a risk-management measure.
The picture of risks to the labor market has changed significantly since the Fed last met. The labor market is cooling, suggesting that now is the time to factor this into policy. We need to remain steadfast in our commitment to returning inflation to 2%.
At the same time, we need to balance the risks to the Fed's two main objectives. Inflation risks have decreased since April. Not all changes in the labor market are due to immigration; demand has clearly slowed. Inflation is expected to rise this year as tariffs increase commodity prices; however, this increase is expected to be a one-time event. Our job is to ensure this is a one-time increase in inflation, and we will accomplish our mission. Cases of sustained inflationary outbreaks are rare. It's time to acknowledge that the risks to the jobs mandate have increased. The only way voters can change the situation is with persuasive evidence based on data. That's how things work. We will use all the tools at our disposal to achieve our goals.
There's widespread agreement that the labor market situation has changed. New data suggests significant downside risks to the labor market, and this is widely acknowledged. Almost everyone wrote in support of this cut. The economy isn't in bad shape. From a policy perspective, it's difficult to know what to do. It's not immediately obvious what to do.
There are two equally important objectives to focus on. The sharp decline in labor supply and demand has everyone's attention. Fortunately, economic activity remains stable, and consumption is holding up quite well. The focus of today's decision is on the risks facing the labor market.
Key Points from the Federal Open Market Committee Statement
Forecasts indicate another 50 basis point rate cut before the end of the year, followed by 25 basis point cuts in each of the following two years. Job growth has slowed, and the unemployment rate has edged up but remains low. Inflation has risen but remains at "slightly elevated levels." Economic growth slowed in the first half of the year. The Fed stated that it is focusing on both aspects of its dual mandate and maintaining the current pace of balance sheet reduction.
Officials' median forecast for the federal funds rate at the end of 2025 is 3.6% (from 3.9%). Officials' median forecast for the federal funds rate at the end of 2027 is 3.1% (from 3.4%). Officials' median forecast for the federal funds rate at the end of 2026 is 3.4% (from 3.6%). Officials' median forecast for the federal funds rate at the end of 2028 is 3.1%. Officials' median forecast for the federal funds rate in the longer run is 3.0% (from 3.0%).
Forecasts indicate another 50 basis point rate hike in 2025, followed by 25 basis point hikes in 2026 and 2027. Nine of the 19 policymakers project two more rate cuts in 2025, two predict one, and six foresee no further cuts. Policymakers project the unemployment rate at the end of 2025 to be 4.5%, unchanged from their June forecast. Forecasts show one policymaker predicting the appropriate policy rate at year-end to be between 4.25% and 4.50%, while another sees it between 2.75% and 3.00%. Policymakers project PCE inflation at the end of 2025 to be 3.0%, unchanged from their June forecast, and core inflation to be 3.1%, also unchanged from their June forecast. Policymakers project GDP growth at 1.6% in 2025, up from their June forecast of 1.4%, with the long-term growth rate remaining at 1.8%, unchanged from their June forecast.
Market reaction to Fed policy
The market had generally expected the Federal Reserve to initiate its first interest rate cut since December last year, lowering the policy rate to the range of 4%-4.25%. The results of the meeting were also in line with previous market expectations.
The market reacted significantly after the interest rate meeting. The selling pressure on the US dollar intensified, hitting a new low for the year. The US dollar index fell accordingly , falling to 96.21 at one point, the lowest since February 2022.
Half an hour later, Powell delivered a speech, emphasizing that "the economy is not bad." The overall wording was less dovish than expected, which re-boosted the market's positive sentiment on the economic outlook. Buying poured into the US dollar, and the US dollar index rebounded , closing up 0.4% on Wednesday. The rebound continued in the Asian session on Thursday, currently trading around 97.19.
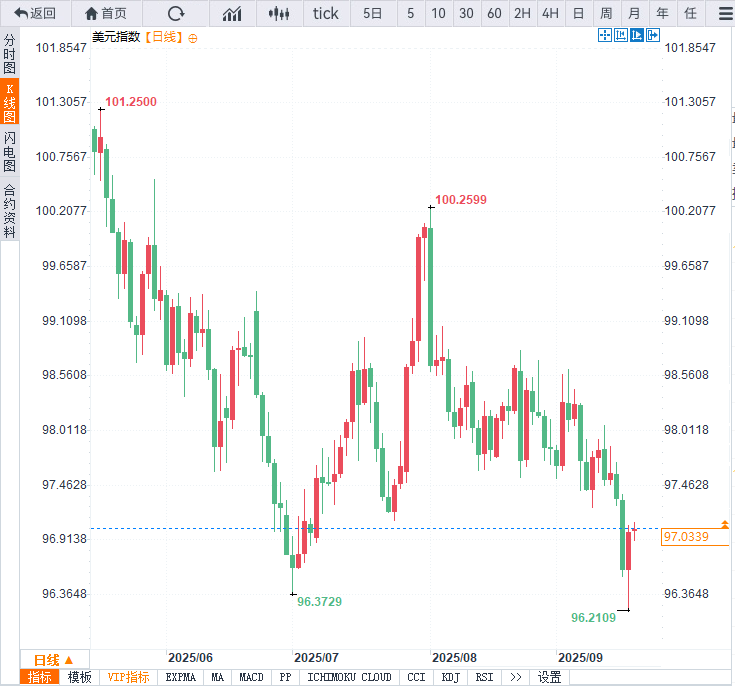
(Daily chart of the US dollar index, source: Yihuitong)
Currently, according to CME's "Fed Watch," the probability of the Fed keeping interest rates unchanged in October is 12.3%, and the probability of a 25 basis point rate cut is 87.7%. The probability of the Fed keeping interest rates unchanged in December is 1.1%, the probability of a cumulative 25 basis point rate cut is 19.0%, and the probability of a cumulative 50 basis point rate cut is 79.9%.
Euro/dollar future trend forecast
FXStreet Chief Analyst Eren Sengezer provides short-term technical analysis of EUR/USD:
“EUR/USD maintains a mildly bullish outlook in the short term. The daily relative strength index (RSI) remains firmly above 50, while the pair is trading above both the 20-day simple moving average (SMA) at 1.1711 and the 50-day SMA at 1.1666.”
“On the upside, the first resistance level is 1.1829 (July 1 high), followed by 1.1900 (static level/round number) and 1.2000 (round number). Downside support is the intersection of the 20-day and 50-day moving averages (1.1711-1.1666), followed by the 100-day moving average at 1.1561.”
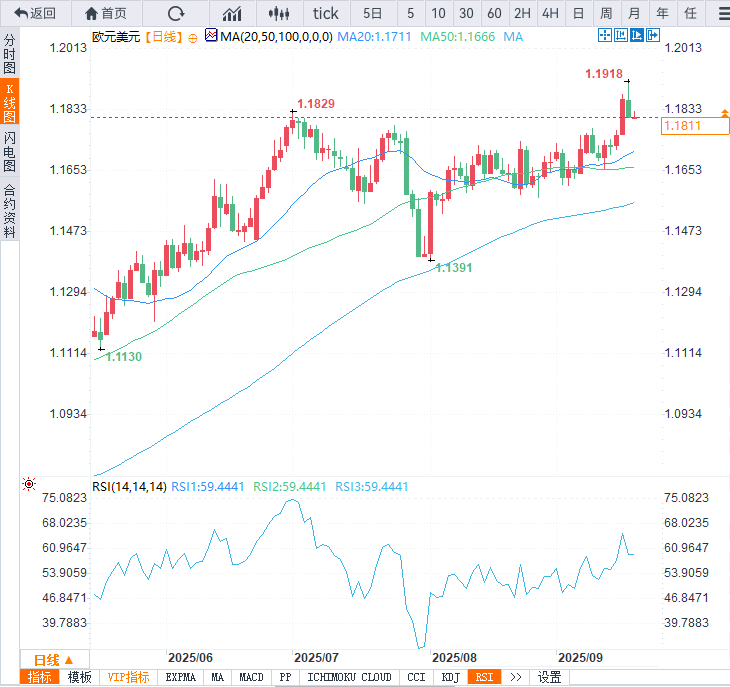
(Euro/USD daily chart, source: Yihuitong)
At 13:44 Beijing time, the US dollar index was at 97.19.
- Risk Warning and Disclaimer
- The market involves risk, and trading may not be suitable for all investors. This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment advice, nor does it take into account certain users’ specific investment objectives, financial situation, or other needs. Any investment decisions made based on this information are at your own risk.





















