Why did gold alone seize the opportunity when everyone was waiting for the US data?
2025-11-25 21:58:03

Market sentiment was cautious ahead of the data release. The 10-year US Treasury yield briefly fell to 4.15%, reflecting investor concerns about an economic slowdown. The US dollar index hovered around 99.90, and spot gold traded at $4,135 per ounce. Analysts generally predicted that retail sales would remain in a moderate growth range of 0.3%-0.4%, with the PPI annual rate remaining stable at 2.6%, supporting the Federal Reserve's gradual interest rate cut path. Some retail traders indicated on social media that strong data could push up the yield curve, but most investors remained cautious.
Market reaction after data release
Following the data release, the US Treasury yield curve rose slightly, reversing the earlier surge in the two-year Treasury yield. The dollar index rebounded 5 points from 99.93, while spot gold rose rapidly by $12 from $4,135 to $4,147 per ounce. This market reaction indicates that investors quickly digested these dovish surprises and are reassessing the outlook for the Federal Reserve's monetary policy. The 10-year Treasury yield stabilized after a brief rise, and the overall yield curve showed signs of flattening, echoing the weak consumption signals in the retail data.
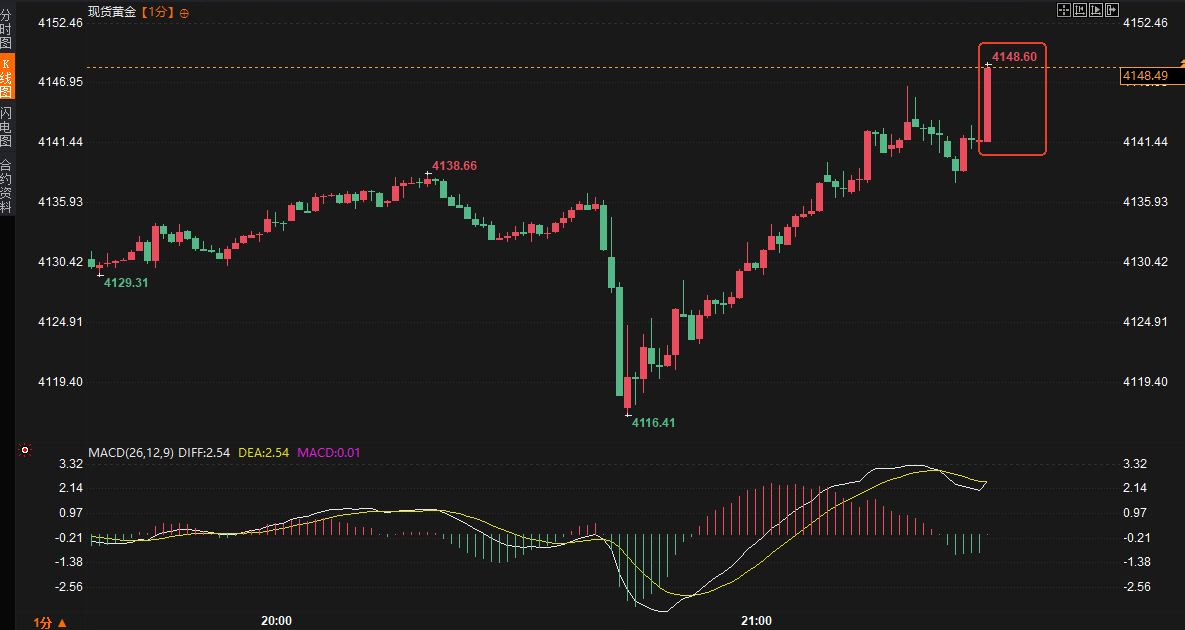
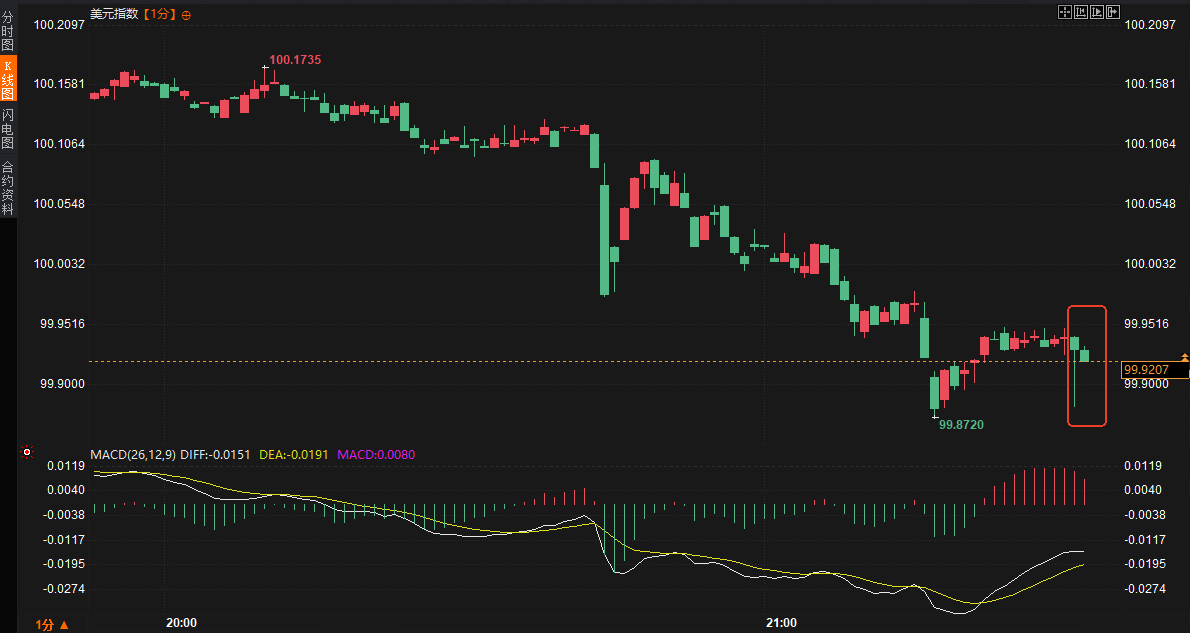
Strengthening expectations of interest rate cuts
From the perspective of Fed rate cut expectations, these data reinforce the likelihood of a December rate cut. Before the announcement, interest rate futures implied a December rate cut probability hovering around 80%. However, today's significant slowdown in retail sales—with core indicators turning negative—directly challenges the assumption of "consumption-driven growth." Economists point out that this may stem from increased spending pressure on low- and middle-income households. The mixed signals from the PPI are even more double-edged: the slight increase in the overall annual rate indicates resilience in energy and commodity prices, but the low level of core indicators suggests that inflation in the service sector has stabilized. The job loss data in the ADP report further amplified this effect, suggesting that while the shutdown effect was short-lived, it exposed concerns about delayed hiring. Taken together, these elements have collectively pushed up the pricing of a rate cut: according to the latest interest rate futures, the probability of a December rate cut has risen to over 85%, 5 percentage points higher than before the announcement.
Market sentiment and platform discussions
The shift in market sentiment was vividly reflected on social media platforms. Before the data release, there was a clear divergence between retail and institutional opinions. Institutional views emphasized that "stronger-than-expected retail sales would strengthen the case for the Fed to pause rate cuts," while retail traders focused more on immediate trading opportunities. After the data was released, the narrative quickly shifted to optimism. Institutional accounts updated their views, stating: "Core PPI cooled to 2.6%, and weak retail data reinforced the weakness in the labor market, making a December rate cut inevitable." Another chief economist commented: "While these lagging data are soft, they are insufficient to change the holiday spending outlook; the key is that they fill the gap in Fed decision-making and support gradual easing." Overall, institutional interpretations focused more on the long-term impact of the data on the economic outlook, while retail traders focused on trading opportunities arising from policy shifts.
Fundamental Analysis and Historical Reference
From a fundamental perspective, while the weak retail data did not shake the overall trend of a consumption recovery in the third quarter, its combination with the ADP employment data outlines a gradually weakening labor market. This aligns with historical patterns: after a similar PPI cooling and retail slowdown in 2019, the Federal Reserve adopted an easing policy. Current data suggests that spending pressures on low- and middle-income households may be increasing, while high-income groups have supported some demand, but the overall economic divergence remains. A breakdown of the PPI data shows that inflation in the service sector has stabilized, which is highly correlated with the PCE index favored by the Federal Reserve.
Policy Outlook and Market Expectations
Looking ahead, market focus will shift to the verification of subsequent economic data. If the December PCE data confirms the PPI trend, the Fed's easing path will become clearer. While the weak ADP employment data requires further confirmation from the non-farm payroll data, it has already shifted market attention from inflation to growth. In the long term, if employment data does not deteriorate further, market expectations for easing policies may continue to strengthen. Overall, although these data are retrospective indicators, they provide important references for the policy path—economic resilience remains, policy space still exists, and investors should use the data as an anchor to prudently assess market risks.
- Risk Warning and Disclaimer
- The market involves risk, and trading may not be suitable for all investors. This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment advice, nor does it take into account certain users’ specific investment objectives, financial situation, or other needs. Any investment decisions made based on this information are at your own risk.





















