Is France's out-of-control debt crisis exacerbating the risk of a "lame-faced" euro?
2025-12-18 16:09:58
While economic growth is expected to recover modestly as inflation eases and financing conditions improve, rating agencies and banks warn that weak fiscal consolidation and legislative gridlock have become structural features of the French economic outlook.

Credit rating agency KBRA downgraded France's long-term sovereign rating to AA- last week, highlighting these concerns. The agency noted persistently high deficits and a deteriorating debt trajectory, and while revising its outlook from negative to stable, warned that without decisive reforms and spending constraints, France's sovereign credit metrics will remain under pressure.
Ken Egan, Senior Director of Sovereign Ratings at KBRA, said: “Despite France’s exceptional access to liquidity, the fragmented political environment is putting pressure on credit metrics by hindering substantive fiscal consolidation and maintaining high deficit levels.”
French economic growth remains moderate
France is facing a delicate period of transition. Economic growth is slowing, debt is rising, and the window for fiscal consolidation before the 2027 presidential election is narrowing.
While the risk of recession remains limited, the space to adjust public finances without disrupting economic activity is increasingly constrained.
KBRA data shows that GDP growth slowed to 1.1% in 2024 and is projected to be around 0.8% in 2025. Output was significantly hampered by weak domestic demand, sluggish investment, and ongoing uncertainty related to geopolitical and trade fragmentation.
Despite declining inflation and improved real wages, household spending remains cautious due to persistently high savings rates.
Investment is also constrained by the lagged effects of interest rate hikes, particularly in construction and other interest rate-sensitive sectors. While the Recovery and Resilience Fund (RRF) and the "France 2030" plan are expected to provide support, the overall impact may be limited without broader reforms.
On the positive side, France's inflation rate has fallen significantly, providing some breathing room for households after a prolonged period of price pressure. By the end of 2025, the harmonized inflation rate for the Eurozone as a whole is projected to fall to 0.9% year-on-year, well below the European Central Bank's target level and also below the Eurozone average.
This rapid disinflation reflects the dual effects of regulated energy price adjustments and controlled wage dynamics.
Political factors hinder the implementation of fiscal policy
The main constraint on fiscal progress lies in France’s increasingly divided political landscape.
President Macron's second term has been plagued by a budget impasse, the loss of his absolute majority in parliament, and increasing difficulty in passing key legislation.
Multiple votes of no confidence and the frequent use of constitutional tools highlight a deeper structural deadlock in policymaking.
Efforts to advance fiscal reforms, including the controversial 2023 pension reform, have been delayed or shelved as the government seeks fragile parliamentary support.
The temporary suspension of pension measures (which were originally expected to save €11 billion annually by 2027) highlights the cost of these political compromises.
The reform and adjustment plan is currently expected to achieve cost savings of 100 million euros by 2026 alone.
KBRA's Egan warned that policy uncertainty is "adding a premium to French sovereign debt," reflecting increasingly cautious investor sentiment. He added that while there may be brief periods of limited political cohesion, "the overall landscape remains deeply divided with little sign of easing and could even worsen further."
Public finances remain a core vulnerability.
The International Monetary Fund predicts that France's debt-to-GDP ratio will rise from about 116% in 2025 to nearly 130% in 2030, running counter to the fiscal consolidation path of most Eurozone countries.
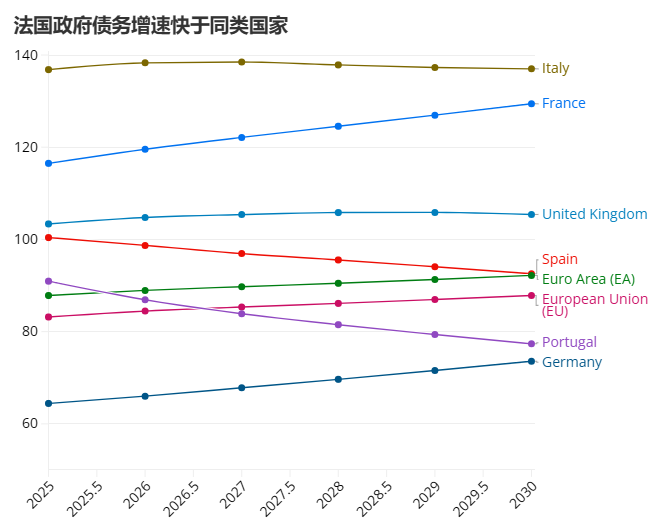
Soaring interest payments are exacerbating the fiscal burden. The French Ministry of Finance projects that debt servicing costs will surge to €59.3 billion in 2026 (compared to €36.2 billion in 2020).
France also continues to face a primary budget deficit, projected to reach 3.4% between 2026 and 2030, which undermines its ability to stabilize its debt trajectory.
In its report, the KBRA warned that "rising financing costs and increased spending pressures mean that genuine fiscal consolidation will require years of sustained effort."
Although government revenue still accounts for more than 51% of GDP, given that France is already one of the OECD countries with the highest tax burden as a percentage of GDP, there is limited room for further increases.
At the same time, structural pressures on spending are expected to persist, particularly in the areas of pensions and defense.
Strong market access offset short-term risks
Despite these weaknesses, KBRA emphasizes that France maintains exceptional financing flexibility. French government bonds benefit from deep liquidity, a diversified investor base, and the country's central role in the Eurozone.
Even amid heightened political uncertainty, these factors continue to support smooth market access.
The KBRA believes that this balance between strong market access and weak fiscal fundamentals will determine France's development prospects toward 2026.
While liquidity has reduced short-term risks, the agency warned that without continued fiscal consolidation and greater political stability, France’s debt burden could continue to rise, limiting medium-term policy flexibility.
France's problems may not cause the euro to collapse, but they could leave it "lame." They label the euro as having "internal governance risks," putting pressure on its long-term valuation and making it more vulnerable to sell-offs during market turmoil.
The euro edged lower against the dollar on Thursday, falling about 0.07%, with market traders focused on the European Central Bank's interest rate decision later that evening.
The future upward momentum of the euro depends not only on the monetary policy of the European Central Bank, but also on whether member states, led by France, can demonstrate genuine fiscal reform and political governance capabilities.
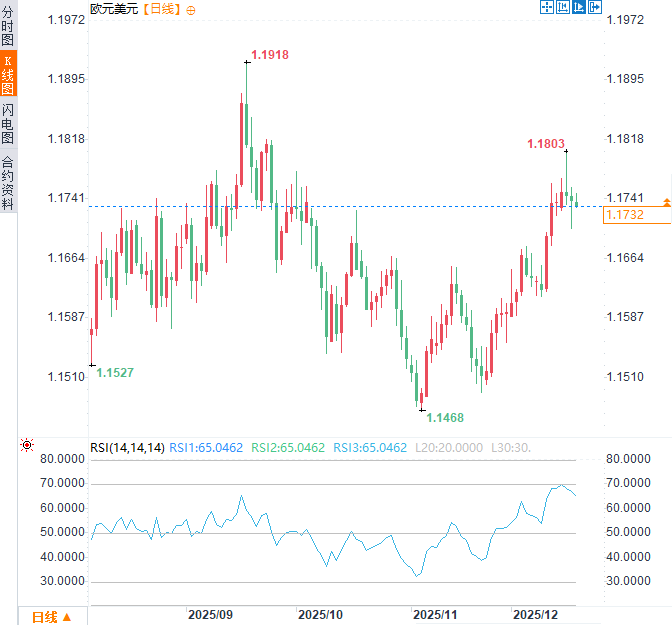
(Euro/USD daily chart, source: FX678)
At 16:03 Beijing time, the euro was trading at 1.1731/32 against the US dollar.
- Risk Warning and Disclaimer
- The market involves risk, and trading may not be suitable for all investors. This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment advice, nor does it take into account certain users’ specific investment objectives, financial situation, or other needs. Any investment decisions made based on this information are at your own risk.