Balance sheet contraction halted, repurchase rates rise: Is the dollar liquidity situation quietly changing?
2025-12-03 21:12:43
Subtle shifts in market sentiment often first manifest in exchange rates. The decline in the US dollar index means that investors' expected returns on dollar assets are no longer as attractive as before. Especially against the backdrop of a potential shift towards more accommodative policies by the Federal Reserve, funds are beginning to reassess the relative advantage of the dollar among global currencies, and demand for safe-haven assets has cooled.
In this environment, any news related to the Federal Reserve's policy direction will be amplified and interpreted by the market. Rumors about the Fed Chair nominee, changes in key economic data, and the tightness of the money market all become "invisible weights" weighing on the dollar.
Hassett Rumors and the FOMC Mechanism: A Game Around "Lower Interest Rates"
Trump has publicly stated that he will nominate a new Federal Reserve Chairman in early 2026, and has named Kevin Hassett, director of the White House National Economic Council, as one of the potential candidates. This statement immediately attracted market attention, as Hassett is considered a more dovish economist who has long advocated for more aggressive interest rate cuts and even emphasized that he is highly aligned with Trump on the view that "interest rates can be lower."
Such expectations are extremely damaging to the US dollar. If the Federal Reserve strengthens its easing stance during Hassett's tenure, the long-term interest rate center may shift downward, further compressing the relative returns of dollar assets. Funds will naturally tend to seek currencies and assets with higher returns or more neutral policies, thereby accelerating the weakening of the dollar.
However, analysts also emphasize that the Federal Reserve Chair does not make decisions alone. The actual decision-making power rests with the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), composed of seven Federal Reserve Governors and five Federal Reserve Bank presidents, each with one vote. Even if the Chair's personal stance is dovish, a majority vote within the FOMC is required for monetary policy to truly shift. Therefore, Hassett's personal inclination is more of a directional signal than an absolute directive.
Economic data and the yield curve: a fundamental explanation for the weakening dollar.
Beyond the rumors surrounding the chairmanship candidate, recent US economic data is subtly reinforcing the narrative of "easing expectations." In the labor market, while the unemployment rate remains relatively low, signs of weakening demand for labor, slower hiring, and cooling wage growth are emerging, suggesting insufficient endogenous growth momentum. Consumer spending has also shown initial signs of weakness, with household spending less robust than previously anticipated.
On the inflation front, while there remains some upward pressure on prices in the short term, overall inflation risks are diminishing, and the inflation level has not yet stably reached the Federal Reserve's target. For the Fed, which has always focused on both inflation and employment, the combination of economic slowdown and easing inflationary pressures objectively leaves room for further interest rate cuts. Based on this, the market has strengthened its bets on future easing policies, thereby exerting sustained downward pressure on the US dollar.
The changes in the US Treasury yield curve provide a direct reflection of the financial market. Recently, the yield curve has shown a trend of short-term yields declining more sharply than long-term yields. This curve shape often indicates two things: firstly, the market expects policy rates to be lowered in the short term; secondly, there is a greater degree of caution regarding long-term economic growth. This expectation structure makes investors more willing to reduce their dollar exposure and seek alternative assets with greater growth potential or higher returns.
Against this backdrop, the weakening of the US dollar is no longer merely a matter of "emotional fluctuations," but rather a result that corroborates economic fundamentals and policy expectations. Analysts believe that as long as there are no clear signs of stabilization in the labor market and on the consumption side, the market's expectation of interest rate cuts will be difficult to narrow, and the dollar's rebound will lack sustained momentum.
Tight liquidity and expectations for policy tools: The short-term outlook for the US dollar remains under pressure.
Beyond the interplay of expectations, the US dollar also faces real pressure on the money supply. The Federal Reserve officially ended its balance sheet reduction on December 1st, signifying the end of the process of withdrawing liquidity through "quantitative tightening." Theoretically, this should help alleviate some of the funding shortage, but the market's actual reaction has been more complex.
Recently, the cost of dollar funding has faced upward pressure, particularly in the repo market, where interest rates have tightened at times. This tightness may indicate structural or risk-averse changes within the market, with some institutions becoming more reliant on short-term dollar liquidity. As repo rates continue to rise, investors begin to speculate whether the Federal Reserve will be forced to stabilize the market by expanding its balance sheet and increasing asset purchases. Once this expectation takes hold, it means that the supply of dollars in the market may increase significantly in the future.
More dollar liquidity does not necessarily translate into a stronger exchange rate. On the contrary, against the backdrop of expectations of interest rate cuts and a weakening interest rate advantage for the local currency, increased liquidity is often interpreted as "strengthened easing," thereby exacerbating downward pressure on the dollar. The tug-of-war between tightening liquidity and expectations of easing measures creates a double squeeze on the dollar: on one hand, there is the current instability of financing costs, and on the other hand, there are concerns about potential future "quantitative easing."
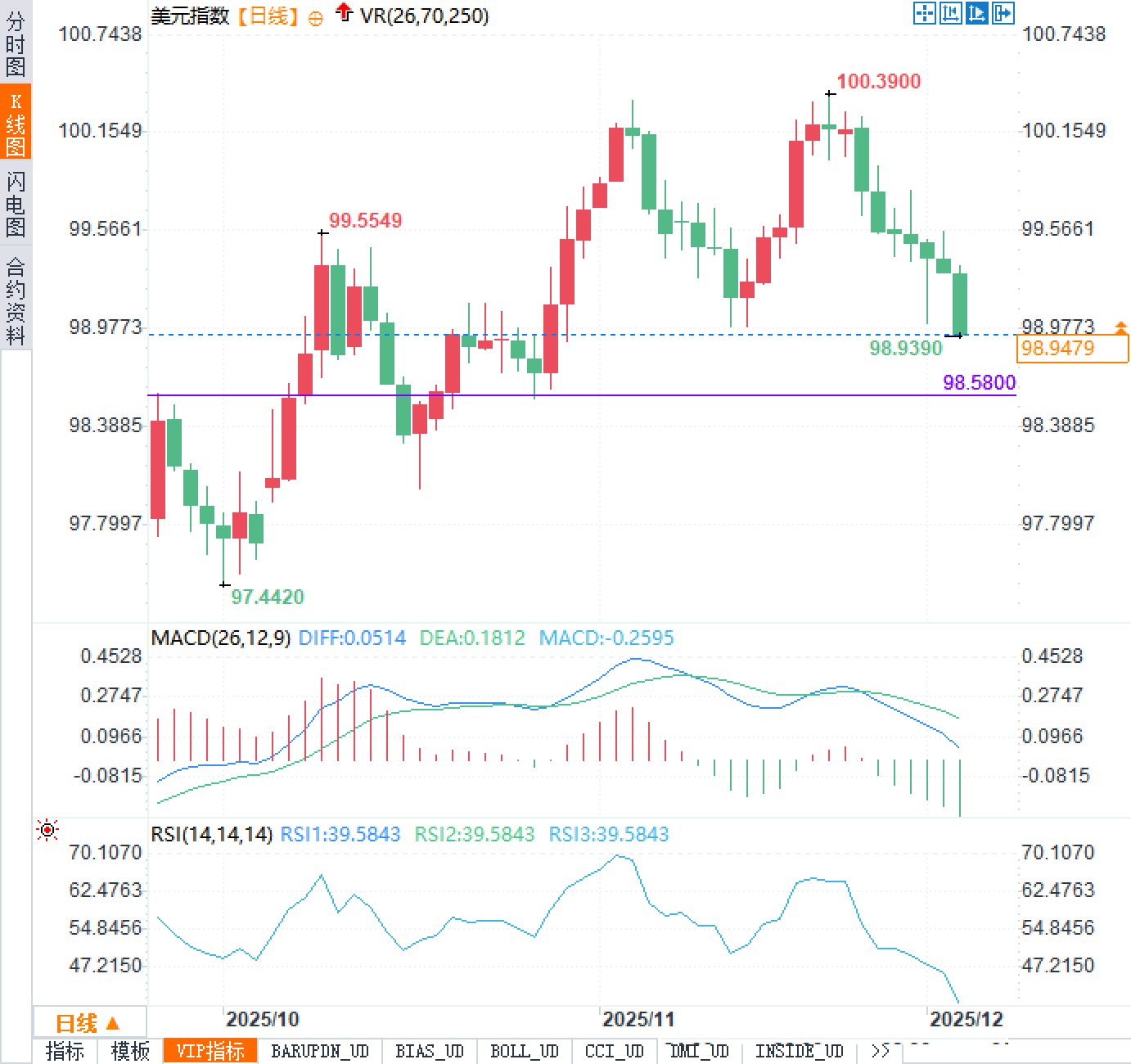
In summary, the US dollar index's hovering around the 99 level is not accidental. A dovish stance on the Federal Reserve chairman nomination, weak US economic data, tight money markets, and expectations of potential asset purchases have all combined to weigh on the dollar. In the short term, analysts generally believe that the dollar will continue to face some downward pressure.
- Risk Warning and Disclaimer
- The market involves risk, and trading may not be suitable for all investors. This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment advice, nor does it take into account certain users’ specific investment objectives, financial situation, or other needs. Any investment decisions made based on this information are at your own risk.





















