Fiscal Expansion Suppresses the Yen: Technical and Fundamental Analysis of USD/JPY
2026-01-23 20:14:05

The yen touched a low of around 159.23 this week, briefly rebounding to 157.37 after the Bank of Japan's (BOJ) policy meeting. However, driven by fiscal concerns, the rebound lacked sustained support. The exchange rate is now approaching the key psychological level of 160, and market expectations for potential government intervention in the market continue to rise.
The Bank of Japan's policy stance is the core source of fundamental pressure on the yen. On January 23, the Bank of Japan maintained its benchmark interest rate at 0.75% by an 8-1 vote, rejecting a proposal from a member to immediately raise rates to 1%. Simultaneously, the central bank raised its GDP growth forecast for fiscal years 2025-2026 to 0.9%-1.0% and revised its core inflation path upward, expecting inflation to remain above the 2% policy target until fiscal year 2027. Governor Kazuo Ueda stated that if economic and price trends meet expectations, the bank will continue its rate hike process, but did not provide a specific timetable, emphasizing the need to first assess the actual impact of the December rate hike. The market interpreted these remarks as slightly hawkish, but they failed to provide sufficient support for the yen in the short term, leading to a volatile exchange rate trend of initial weakness followed by a rebound after the meeting. Analysts generally believe that the Bank of Japan needs to release a clearer hawkish signal to effectively reverse the yen's weakness; the market has already priced in approximately two rate hikes in 2026, with some institutions expecting up to three.
Expectations of fiscal expansion and political risks have become key variables driving the yen's current exchange rate. Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi formally dissolved the House of Representatives on January 23, with a snap election scheduled for February 8. Takaichi pledged to end "excessive austerity" policies, including suspending the food consumption tax for two years (estimated to result in a 5 trillion yen tax revenue loss) and pushing for larger-scale economic stimulus spending. This statement exacerbated market concerns about Japan's fiscal deficit—currently the highest among developed countries—leading to significant volatility in the Japanese bond market: the 40-year government bond yield broke through 4%, reaching a record high, while 10-20 year government bond yields also rose sharply. Although Takaichi's personal approval rating remains high, indicating her intention to consolidate power through the election, the overall polling performance of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) is weak, and the uncertainty surrounding the election outcome further amplifies selling pressure on the yen. Currently, concerns about fiscal dominance have overshadowed interest rate differentials, becoming the primary reason dragging down the yen's exchange rate.
The yen's weakness has deepened since Kao Shih took office in October, during which time it has depreciated by more than 7% against the US dollar. Despite the prospect of a Bank of Japan interest rate hike, selling pressure in the bond market triggered by expectations of fiscal easing has significantly weakened the yen's safe-haven appeal. Strategists warn that a break above the 160 level could trigger government intervention, and the Japanese Finance Minister has already verbally warned that he "will not rule out any means" to address speculative exchange rate fluctuations.
If Kaohsiung's Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) achieves a landslide victory in the general election (e.g., securing a majority of seats in parliament), many analysts believe this will further strengthen the expansionary fiscal policy orientation, accelerating the weakening of the yen. Strategists at MUFG and SMBC Nikko point out that after a confirmed landslide victory, market concerns about Kaohsiung's increased fiscal expansion with public support will intensify, accelerating yen selling and increasing upward pressure on USD/JPY. Junya Tanase, head of foreign exchange strategy at JP Morgan, believes that after Kaohsiung clarifies the details of its expansionary policy, the yen's fundamental weakness will continue, and USD/JPY is expected to rise to 164 by the end of 2026. Nomura and Pepperstone believe that Kaohsiung's reflationary policy orientation will suppress the yen's performance, providing support for the stock market but exacerbating the steepening of the yield curve. Analysts at Orbex believe that a landslide victory will cause the yen to weaken slightly, the extent depending on the details of the economic plan, and may reactivate carry trades.
Another view holds that a landslide victory in the election may lead to a short-term depreciation of the yen by more than 2%, but if the Kaohsiung City government implements "responsible and proactive fiscal policy," it may be able to limit the depreciation and alleviate further downward pressure. In the medium term, if the Bank of Japan accelerates interest rate hikes due to inflation remaining above 2%, it is expected to partially offset the drag on the yen from fiscal expansion.
In the coming days, US economic data is relatively light, mainly focusing on the manufacturing and real estate sectors. The preliminary reading of the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index for January, to be released tonight, is the most closely watched data in the short term. An unexpected rise in confidence could alleviate market concerns about a US economic slowdown, thus providing some support for the dollar. In addition, the Dallas Fed Manufacturing Activity Index early next week will also provide clues about the regional manufacturing climate, but its impact is relatively limited, serving more as a sentiment driver. Overall, the data in the coming days is expected to have a moderate impact on the market and is unlikely to trigger significant volatility on its own. In the absence of major data releases, the USD/JPY exchange rate is more likely to continue to be driven by Japanese fiscal and political risks, changes in US Treasury yields, and expectations of intervention.
In the short term, the weak yen will continue to dominate the market, with a target range of 159-160+. Fiscal and political risks will outweigh the Bank of Japan's hawkish stance, keeping the risk of intervention high. In the medium term, if Kaohsiung wins the general election, fiscal expansionary policies will continue to suppress the yen, potentially pushing the exchange rate towards the 160-164 range. However, the Bank of Japan's interest rate hike path (if inflation remains above 2%) will provide potential support for the yen. It is recommended to closely monitor the election results on February 8th and this week's core US economic data (especially core PCE). If the exchange rate breaks through the 160 level, the probability of Japanese government intervention will increase significantly.
Technical Analysis
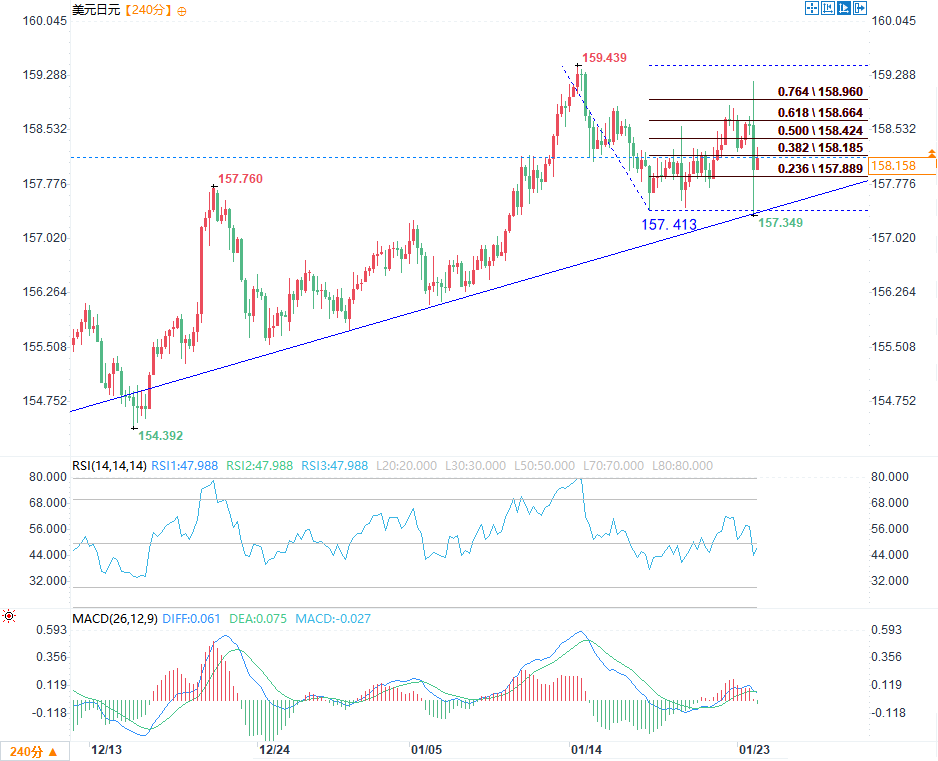
(USD/JPY 4-hour chart source: EasyForex)
The USD/JPY pair stabilized around 157.41, and after forming a bottom, it began a new round of gains, breaking through the 158.00 level.
From the 4-hour chart, the exchange rate has climbed above 158.20, breaking through the 50% Fibonacci retracement level (158.42) of the downtrend from the high of 159.43 to the low of 157.41. Currently, the exchange rate is firmly above the short-term moving averages on the 4-hour chart.
Short-term resistance:
Initial resistance is around 158.96, which is also the 76.4% Fibonacci retracement level of the decline from the high of 159.43 to the low of 157.41.
If the closing price rises above 158.96, it may open up upward potential, targeting the previous high of 159.43; further gains could initiate a steady upward trend.
Downside risks:
If it fails to break through 158.96, it may trigger a new round of pullback.
Initial support is at 158.18 (0.382 Fibonacci retracement level), with the first key support zone for the bulls around 158.00, which is also the support level of a major uptrend line.
If the closing price falls below 158.00, it could trigger a sharp decline, with the next support level at 157.89 (the 0.236 Fibonacci retracement level). If this level is broken, the bears may push the price further down to the previous low of 157.41.
- Risk Warning and Disclaimer
- The market involves risk, and trading may not be suitable for all investors. This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment advice, nor does it take into account certain users’ specific investment objectives, financial situation, or other needs. Any investment decisions made based on this information are at your own risk.















